Have you ever heard about marijuana and alcohol withdrawal symptoms? In the modern, world where stress is an unwelcome but persistent friend, many people find comfort in body-destroying substances such as alcohol and marijuana. These are not just meant to smoothen social interactions – instead, they become methods for relaxing or getting away from problems.
However, this relaxation is short-lived and can sometimes result in a more complicated condition called alcohol use disorder or dependency on marijuana. These are not simply habits but also recognized medical conditions that impact a large number of people within the U.S.
If a person makes up their mind to reduce or give up, they could have an unexpected visitor: withdrawal. Understanding how to cope with these syndromes is very important. It’s the initial stage in dealing with them correctly and taking back power over your health and life. Let’s take a closer look at marijuana and alcohol withdrawal symptoms.

Understanding Substance & Drug Withdrawal Syndromes
Withdrawal syndrome is a group of symptoms that appear when someone cuts back or quits using a substance their body has adjusted to. This condition emphasizes how the body readjusts to the absence of something it has gotten used to. Picture your brain as a seesaw and these substances help keep you balanced. The sudden withdrawal of them causes everything to become unsteady and results in physical and mental effects as your body and mind try to find the balance once again.
Why Do Withdrawal Symptoms Happen?
As time passes, the brain becomes dependent on these substances to make certain chemicals or activate particular receptors. Alcohol, for example, depresses the nervous system and when you drink it often enough, your body reacts by becoming more alert. Take away alcohol, and the body overcompensates. This is why some people get anxious, and experience shaking or more serious side effects.
In a similar way to alcohol impacting GABA receptors, marijuana influences the brain’s receptors that control mood, perception, and pain. The cessation of its use can cause these receptors to be temporarily disturbed, leading to marijuana withdrawal symptoms.
Marijuana Withdrawal Syndrome – Symptoms and Timespan
Marijuana, or cannabis (THC), is a drug frequently used in the United States being available for both medical and personal use. Marijuana Withdrawal Syndrome (MWS) is a group of symptoms that may happen when someone who regularly uses marijuana abruptly stops or greatly decreases their consumption. The intensity of MWS can vary from light to severe and affects a person’s physical and mental well-being.
Most common physical symptoms:
- Headaches;
- Sweating;
- Tremors;
- Nausea and vomiting;
- Abdominal pain;
- Chills;
Most common psychological symptoms:
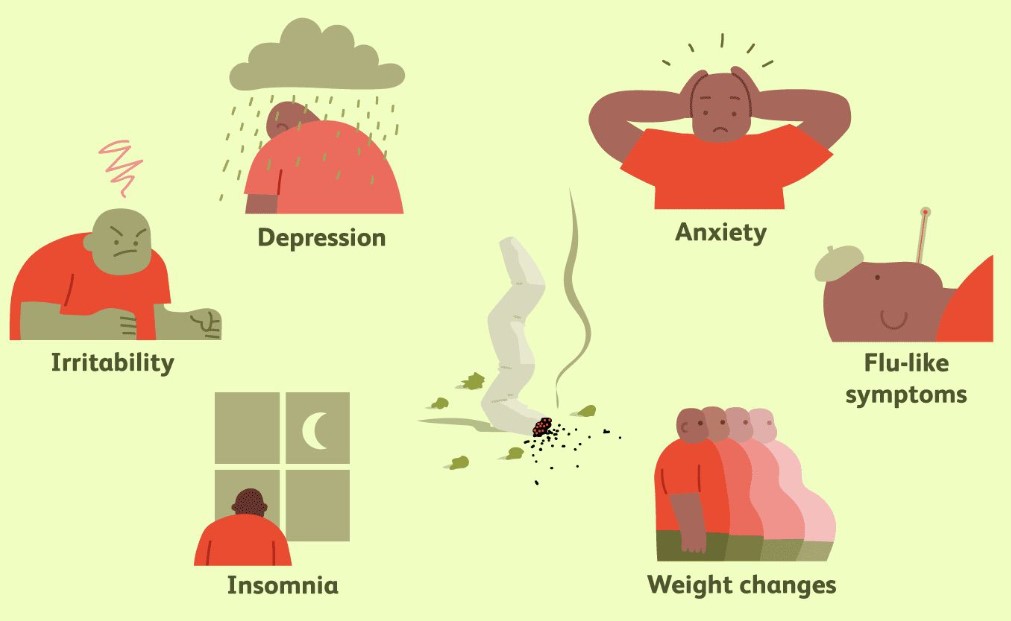
- Irritability and anger;
- Anxiety and restlessness;
- Insomnia or vivid dreams;
- Depression;
- Difficulty concentrating;
- Cravings for weed use:
How Long Do Marijuana Withdrawal Symptoms Last?
The timespan of MWS might be different for every person. Generally, most people encounter the worst symptoms after they stop using it, within the initial week. Symptoms usually reach their highest point during 48 to 72 hours and then slowly lessen over a few weeks.
Sometimes, the severe symptoms could last for a few months. This is particularly true in people who have been heavy substance users for a long time.
According to the research provided by the reputable Oxford Treatment Center, you should expect the marijuana withdrawal symptoms to occur and last in such a way:
| Timespan | Symptoms During This Period |
| First 3 days | Vomiting, stomach pain, excessive perspiration, restlessness, physical craving for marijuana |
| 7-10 days | Physical symptoms start to taper off, psychological symptoms intensify, depression |
| 10-20 days | Symptoms begin to reduce |
| Up to 30 days | Insomnia, lethargy, fatigue |
| 30 days + | Anxiety, depression |
Alcohol Withdrawal Syndrome – Symptoms and Timespan
Alcohol, a substance that is legal and extensively used, can cause dependency if consumed in large amounts. Alcohol Withdrawal Syndrome (AWS) is a group of signs that happen when someone who has been drinking much for a long time suddenly stops or greatly lessens their intake of alcohol. These symptoms might range in intensity from slight to severe and can even be dangerous to life sometimes.
Most common physical signs of alcohol withdrawal:
- Tremors or “alcohol shakes”;
- Headaches;
- Sweating;
- Nausea and vomiting;
- Rapid heart rate;
- Increased blood pressure;
Most common psychological signs of alcohol withdrawal:
- Anxiety and irritability;
- Confusion;
- Insomnia or vivid dreams;
- Depression;
- Difficulty concentrating;
- Cravings for alcohol;
Important notice: in certain situations, discontinuing alcohol use can bring about a critical condition known as delirium tremens (DTs). DTs require immediate medical attention and can be fatal if left untreated.
Symptoms associated with DTs could be:
- Severe confusion and disorientation;
- Hallucinations;
- Fever;
- Seizures;
- Extreme agitation;

How Long Do Alcohol Withdrawal Symptoms Last?
The timespan for alcohol withdrawal symptoms is not fixed, it relies on aspects like how long and intense someone has been using alcohol. Generally, these signs start showing up after 6-24 hours of the last drink and can worsen during 24-72 hours. Most symptoms go away within one week but some of them might continue for a few weeks or months.
The AWS may cause symptoms that last from 6 hours to a few months. Here is what you should expect:
| Timespan | Symptoms During This Period |
| First 6-12 hours | Anxiety, headache, shaking, nausea, vomiting, insomnia |
| 12-24 hours | Disorientation, hand tremors, seizures (in severe cases) |
| 24-48 hours | Seizures, hallucinations, high blood pressure, heavy sweating |
| 48-72 hours | Delirium tremens (DTs) – confusion, rapid heartbeat, fever, heavy sweating |
| Up to 1 week | Mood swings, fatigue, continued sleep disturbances |
| Several weeks-months | Anxiety, depression, irritability, continued sleep disturbances, decreased energy |
How to Detox From Weed – Possible Treatment Options
If you are experiencing Marijuana Withdrawal Syndrome (MWS), understand that many people go through this and there are different treatments to assist in handling your symptoms and staying away from weed. These methods include non-pharmacological therapies, medicines, and changes in lifestyle along with home-based solutions.
Non-Pharmacological Treatment
- Cognitive-behavioral supportive therapy guides you in recognizing and modifying harmful thinking patterns and actions linked to marijuana consumption;
- Motivational enhancement therapy can assist you in enhancing your motivation to modify marijuana use behaviors and create a roadmap for healing;
- Contingency management uses rewards to encourage abstinence from marijuana;
- You may find it helpful to become part of a support group like Marijuana Anonymous. This can offer you a feeling of belonging and let you interact with people who are also striving for abstinence;
Pharmacological Treatment
- Over-the-counter or prescription sleep medications may help with insomnia and sleep disturbances;
- If you experience depression or anxiety in the withdrawal period, your doctor might give you a prescription for antidepressants to assist in handling these symptoms;
- Sometimes, quitting marijuana can lead to seizures. Anticonvulsant drugs work well in stopping and preventing these seizures from happening;
Lifestyle Changes and Home Remedies
- Physical activity can boost your mood, reduce stress, and improve sleep quality;
- Deep breathe, meditate, and do gradual muscle relaxation to handle anxiety and being easily annoyed;
- Having a balanced diet that contains lots of fruits, vegetables, and whole grains can aid your body in handling the process of withdrawal;
- Drinking enough water can ease headaches and lessen the possibility of getting dehydrated;
- Try to find fresh hobbies or rekindle past interests that can divert your attention from cravings;
How to Detox From Alcohol – Possible Treatment Options
AWS is a difficult and possibly hazardous condition, but with correct treatment and help from others, it can be overcome. The usual treatment for alcohol detox involves a mix of medications, pill interventions, supportive care as well as long-lasting rehabilitation methods.
Pharmacological Alcohol Withdrawal Syndrome Treatments
- Benzodiazepines: Medications like diazepam (Valium) or lorazepam (Ativan) can decrease anxiety, tremors and the chance of seizures;
- Thiamine (Vitamin B1): Alcohol intake may result in a lack of thiamine, which could induce neurological issues. Detox frequently includes giving extra thiamine to avoid these complexities;
- Antiepileptic Drugs: Alcohol detox medications such as gabapentin or carbamazepine could be employed to stop or cure seizures linked with alcohol withdrawal;
Lifestyle Changes
- Adequate fluid intake is essential to prevent dehydration and electrolyte imbalances;
- Eating a balanced diet full of vitamins and minerals can aid the body in healing;
- Getting enough sleep and rest can assist in body healing and lessen the intensity of withdrawal signs;
Long-Term Rehabilitation
Detoxing substances and medical management are very important for treating the immediate symptoms of alcohol withdrawal, but continuous rehabilitation is necessary to keep sobriety and avoid falling back into old habits.
Here are a few long-term treatment methods that have been successful:
- Cognitive-behavioral therapy (CBT): This is the best way to detox from alcohol because CBT assists people in recognizing and modifying harmful patterns, as well as actions related to alcohol abuse;
- Motivational interviewing is a style of counseling that aids people in examining and resolving their mixed feelings regarding their drinking routine;
- Help groups. You may also find it useful to become a part of a help group, like Alcoholics Anonymous (AA) or SMART Recovery. Such groups can offer community and responsibility in keeping sobriety;
- Alcohol detox medications such as naltrexone or acamprosate, used with therapy and group support, can help lessen cravings and avoid relapse;
Start by googling the “alcohol withdrawal centers near me” and get professional assistance if you feel like you can’t cease drinking alcohol on your own. These centers can be even covered by medical insurance, though there are governmental free-of-charge programs and private institutions.
The specialists will help to compile the best alcohol detox program, especially for you.
Comparison of Marijuana and Alcohol Withdrawal
MWS is usually not as serious as AWS. Commonly, people who stop using marijuana might experience irritability, problems with sleep, less desire to eat, and mood changes. Yet, withdrawal from alcohol can lead to more extreme effects such as shaking hands (tremors), fits (seizures), or even dangerous situations like delirium tremens that can be life-threatening.
Treatment for MWS usually concentrates on non-pharmacological methods like counseling, support groups, and altering lifestyles. Certain kinds of medicine might be utilized to handle particular symptoms. However, there are no officially approved FDA medicines made especially for treating withdrawal symptoms related to marijuana.
However, the standard alcohol withdrawal treatment frequently needs medical detoxification and the usage of drugs such as benzodiazepines to control symptoms and avoid issues. Rehabilitation over a long period for alcohol addiction might also include medication-supported treatment (MAT) which decreases cravings and stops relapse. It is specifically important to use the correct program with carefully picked alcohol detox drugs.
So, the difficulties of marijuana and alcohol withdrawal are different. For marijuana, symptoms can be unpleasant but usually not dangerous to life. On the other hand, alcohol withdrawal is more severe and can lead to serious health issues like seizures or delirium tremens. Sometimes, heavy substance users may require emergency alcohol detox in medical institutions. That is why an alcohol drinker needs to get professional medical assistance when they try to stop drinking alcohol because it is not safe for them to do so without help.
How to Prevent Relapse After the Substance Withdrawal?
- Understand what situations, individuals, or feelings might cause cravings. Make a strategy to prevent or handle these triggers;
- Create a circle of friends, family, and others who are strong supporters and comprehend your journey toward recovery; they can offer you motivation as well as responsibility;
- Long-lasting therapy might aid in the improvement of coping strategies, handling hidden problems, and keeping up with enthusiasm toward sobriety;
- Stress is a typical factor that can lead to relapse. It is crucial to learn how to handle stress by engaging in physical activities, meditation or at least doing deep breaths;
- Do the routine things that help with physical, mental, and emotional health like light exercising, eating good food, and getting enough sleep;
- Going to meetings of support groups like Marijuana Anonymous or Alcoholics Anonymous can give you a feeling of belonging and make sure you are committed to your recovery goals;
The road to recovery lasts a lifetime. It’s necessary for people who have experienced withdrawal from any substance use and rehab to continue engaging in ongoing treatment activities.
Conclusion
Marijuana and alcohol withdrawal can be tough and unpleasant conditions for those people who become dependent on these substances. Even though marijuana withdrawal is usually not as serious as alcohol withdrawal, both conditions might cause different physical and mental effects.
Consulting healthcare professionals or addiction experts is very important when dealing with withdrawal symptoms seriously. Treatment methods might consist of different types of medical actions, therapy sessions, support groups, and lifestyle changes, according to each person’s needs and situation.
To people and families who are experiencing marijuana and alcohol withdrawal – recovery is real and there should be no shame in seeking help from other people, especially professionals. Your most important task is to stay healthy!